| Major Groups > Gilled Mushrooms > Pale-Spored > Russula > Foetid Russulas > Russula foetentula |

|
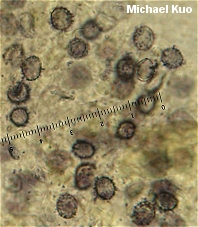
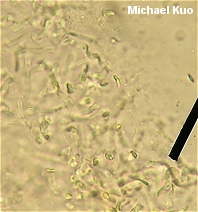
Russula foetentula [ Basidiomycetes > Russulales > Russulaceae > Russula . . . ] by Michael Kuo Separating Russula foetentula from two similar members of the foetid russulas group, Russula fragrantissima and Russula laurocerasi, is likely to require microscopic analysis--though the two competitors are usually more of a dull yellow, while Russula foetentula tends to be pale orangish brown or pale yellowish brown. The microscopic separator is the absence of frequent connecting lines between warts on the spores; the other two species feature such lines much more prominently. Russula subfoetens is a European species; its name is often applied to the North American mushroom featured here. Description: Ecology: Mycorrhizal with hardwoods or conifers; growing alone, scattered, or gregariously; summer and fall; widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains. Cap: 4-12.5 cm; convex with a tucked-under margin when young, becoming broadly convex to flat with a shallow depression; slimy when wet and fresh; pale orangish brown, pale yellowish brown, or sometimes yellowish; the margin lined; the skin peeling away easily at the margin, sometimes beyond halfway to the center. Gills: Attached or pulling away from the stem; close or nearly distant; sometimes forked near the stem; yellowish white; often spotting or discoloring yellowish brown to brownish. Stem: 5-11.5 cm long; 1.5-3.5 cm thick; white, discoloring yellowish to brownish, especially near the base; dry; often becoming cavernous; more or less smooth. Flesh: White; unchanging. Odor and Taste: Odor weakly to moderately or strongly foul, reminiscent of maraschino cherries, almonds, or benzaldehyde; taste slightly to strongly acrid, with an oily component. Chemical Reactions: KOH on cap surface negative to dull orangish. Iron salts on stem surface negative. Spore Print: Creamy to pale yellow. Microscopic Features: Spores 6-9 x 5.5-8 µ; broadly elliptical or nearly round; with warts up to 1 µ high, connecting lines present but scattered, only occasionally forming a partial reticulum. Pleurocystidia positive in sulphovanillin. Pileipellis a cutis; clearly defined pileocystidia absent, but some hyphal tips positive in sulphovanillin. REFERENCES: Peck, 1907 (Saccardo, 1912; Kauffman, 1918; Shaffer, 1972; Smith, Smith & Weber, 1979; Kibby & Fatto, 1990; Phillips, 1991/2005; McNeil, 2006.) Herb. Kuo 07099503, 09099602, 06200306, 07250702. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2009, March). Russula foetentula. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/russula_foetentula.html |