| Major Groups > Jelly Fungi > Helvellosebacina concrescens |

|
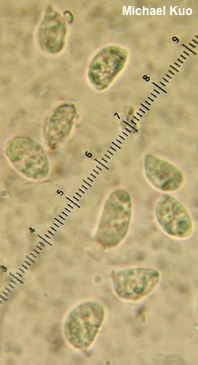
Helvellosebacina concrescens [ Basidiomycota > Sebacinales > Sebacinaceae > Helvellosebacina ... ] by Michael Kuo This jelly fungus is one of only a few that arise from the ground. However, Helvellosebacina concrescens is so formless that once it has appeared, it finds plant stems to attach itself to in order to climb above the forest floor and create enough of a surface area to produce spores. This habitat (clinging to the bases of plant stems), along with the whitish color of the vaguely lobed fruiting body, will serve to separate Helvellosebacina concrescens from most look-alikes. Sebacina incrustans can look similar; however, the latter species is only a few millimeters thick, not as globular, and engulfs not only plant bases, but also sticks, leaves, and anything else it encounters. Tremella concrescens and Sebacina concrescens are former names. Description: Ecology: Mycorrhizal with hardwoods; growing in amorphous masses that climb from the ground, up the stems of plants; summer and fall, or occasionally over winter in warm climates; widely distributed in North America from the Great Plains eastward, southward into Mexico; also known from South America. The illustrated and described collections are from Illinois. Fruiting Body: An amorphous, vaguely lobed mass of material 2–10 cm across; usually 0.5–1 cm thick; surface bald, moist when fresh, pale watery gray to whitish; flesh gelatinous, watery whitish; drying to brown. Odor: Not distinctive. Microscopic Features: Spores 10–16 x 4–6.5 µm; amygdaliform becoming widely allantoid, ellipsoid, or irregular; smooth; hyaline in KOH; walls cyanophilic. Probasidia 9–15 µm across; pyriform (above the pedestal subglobose to ovoid); smooth; hyaline in KOH; becoming cruciate. Basidia 10–15 x 12–18 µm; 4-sterigmate, with long, fingerlike sterigmata (to about 80 µm long). Hyphae 2–4 µm wide; often branched; septate; smooth; hyaline in KOH. Clamp connections not found. REFERENCES: (Schweinitz, 1822) Oberwinkler, Garnica & Riess, 2014. (Martin, 1952; Lowy, 1971; Smith, Smith & Weber, 1981; Weber & Smith, 1985; Barron, 1999; McNeil, 2006; Oberwinkler et al., 2014; Woehrel & Light, 2017.) Herb. Kuo 08080903, 09021904, 08012005. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2020, July). Helvellosebacina concrescens. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/helvellosebacina_concrescens.html |