| Major Groups > Boletes > Suillus > Suillus decipiens |

|
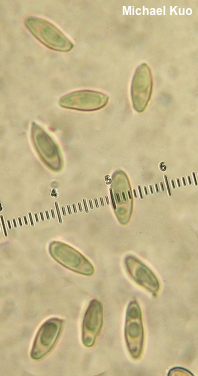
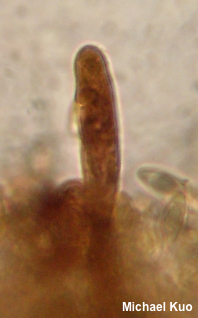
Basidiomycota > Boletales > Suillaceae > Suillus . . . Suillus decipiens by Michael Kuo, 26 April 2023 This southeastern species reminds me of a faded Suillus spraguei or Suillus lakei. The cap is a dull pinkish orange, providing a subtle but attractive contrast with the yellow pore surface. Like its more brightly colored counterparts, Suillus decipiens has a dry cap—a welcome relief in a genus filled with slimeballs. Further distinguishing features include the large, radially oriented pores on mature specimens, and the absence of any blue staining. Look for Suillus decipiens under 2- and 3-needle pines (especially loblolly pine and shortleaf pine) in the southeastern United States, Mexico, and Central America. Thanks to Sister Mary Philomena, O. P., for documenting, collecting, and preserving Suillus decipiens for study; her collection is deposited in The Herbarium of Michael Kuo. Description: Ecology: Mycorrhizal with hard pines (species of Pinus with needles in bundles of 2 or 3), including loblolly pine and shortleaf pine; growing scattered or gregariously; summer, fall, and winter; originally described from South Carolina (Berkeley & Curtis 1853); distributed in North America from roughly New Jersey to Florida and Mexico; also found in Central America and the Caribbean. The illustrated and described collections are from Texas. Cap: 3.5-7 cm; convex becoming broadly convex or flat; dry; yellowish to dull cinnamon or dull orange under small, brownish yellow fibers and scales; often with whitish to yellowish or grayish partial veil remnants on the margin. Pore Surface: Yellowish, becoming brownish yellow; not bruising, or bruising faintly brownish; pores angular, to 1 mm across, radially arranged; tubes to 6 mm deep; initially covered by a whitish to pale yellow partial veil. Stem: 3-7 cm long; up to 1.5 cm thick; more or less equal; dry; finely hairy; yellowish to orangish or brownish; occasionally with a fragile ring; without glandular dots; basal mycelium whitish to yellow. Flesh: Whitish to yellowish; not staining on exposure, or staining slowly pinkish. Odor and Taste: Not distinctive. Chemical Reactions: Ammonia rusty brown, then grayish lilac on cap surface; rusty brown, then blackish on flesh. KOH greenish black on cap surface and flesh. Iron salts slowly black on cap surface and flesh. Spore Print: Brown. Microscopic Features: Spores 7–10 x 2.5–3.5 µm; boletoid-fusiform; smooth; dull golden in KOH. Basidia 28–32 x 4–5 µm; subclavate; 4-sterigmate. Cystidia 40–55 x 5–7.5 µm; cylindric to subfusiform; smooth; thin-walled; hyaline to yellowish or brown in KOH. Pileipellis an ixocutis; elements 3–10 µm wide, smooth, hyaline to yellowish or brown in KOH. REFERENCES: (C. H. Peck, 1889) K. E. O. Kuntze, 1898. (M. J. Berkeley & M. A. Curtis, 1853; Singer, 1945; Smith & Thiers, 1964; Snell & Dick, 1970; Smith, Smith & Weber, 1981; Weber & Smith, 1985; Phillips, 1991/2005; Metzler & Metzler, 1992; Both, 1993; Bessette, Roody & Bessette, 2000; Miller & Miller, 2006; Ortiz-Santana et al., 2007; Klofac, 2013; Bessette et al., 2016; Nguyen et al., 2016.) Herb. Kuo 12172201. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2023, April). Suillus decipiens. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/suillus_decipiens.html |