| Major Groups > Gilled Mushrooms > Pale-Spored > Milky Caps > Lactifluus caeruleitinctus |

|
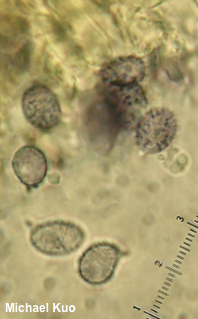
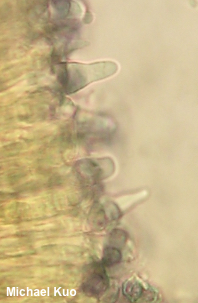
Lactifluus caeruleitinctus [ Basidiomycota > Russulales > Russulaceae > Lactifluus . . . ] by Michael Kuo This southeastern milky cap is a dead ringer for Lactifluus deceptivus; like the latter species, Lactifluus caeruleitinctus has whitish colors, white milk, and an acrid taste. However, Lactifluus caeruleitinctus does not feature the strongly inrolled, cottony cap margin of Lactifluus deceptivus. It also has smaller spores with different ornamentation—and, most notably, its stem develops bluish shades (hence the species epithet caeruleitinctus, "blue tinted"), especially near the apex. Thanks to Andy Methven for facilitating study of Lactifluus caeruleitinctus. Description: Ecology: Mycorrhizal with southern live oak; growing gregariously; fall and winter; originally described from Florida; precise distribution uncertain, but probably to be expected throughout the range of southern live oak. The illustrated and described collections are from Georgia. Cap: 6–9 cm; shallowly depressed, with a slightly tucked-under, uplifted margin that exceeds the gills by a few mm; dry; finely appressed-fibrillose; whitish to brownish, without concentric zones of color; staining slightly pinkish or brownish. Gills: Broadly attached to the stem or just beginning to run down it; close; short-gills infrequent; whitish; staining and bruising pinkish brown to brownish. Stem: 3–5.5 cm long; 1.5–2 cm thick; equal; bald; without potholes; dry; white, with a pale bluish zone at the apex and blue-gray tints near the base; staining pinkish to brownish. Flesh: White; not staining, or staining pinkish when sliced. Milk: White; not staining surfaces. Odor and Taste: Odor unpleasant (Murrill wrote "I have no word for the sickening odor developed in the electric drier" in his 1939 original description of the species), or not distinctive. Taste slowly acrid Microscopic Features: Spores 8–11 x 5–7 µm; ellipsoid; ornamentation consisting of amyloid spines and rods extending up to 0.5 µm high, mostly isolated but sometimes connecting to make small broken reticulated areas. Hymenial macrocystidia 40–55 x 7–10 µm; lageniform to fusiform. Pileipellis a cutis of thin-walled elements 3–5 µm wide, smooth, hyaline or faintly brownish in KOH. REFERENCES: (W. A. Murrill, 1939) L. Delgat, 2019. (Kimbrough, 1972; Hesler & Smith, 1979; Bessette et al., 2009; Delgat et al., 2019.) Herb. Kuo 10092001 (portion of ASM 12486), 11262001 (portion of ASM 12513). This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2020, December). Lactifluus caeruleitinctus. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/lactifluus_caeruleitinctus.html |