| Major Groups > Gilled Mushrooms > Pale-Spored > Tricholoma > Tricholoma equestre |

|
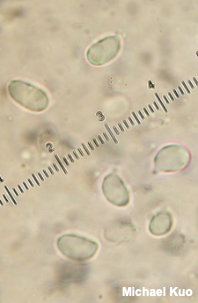
[ Basidiomycota > Agaricales > Tricholomataceae > Tricholoma . . . ] Tricholoma equestre by Michael Kuo, 22 January 2024 Tricholoma equestre can be recognized through a combination of features. It has the white spore print, notched gills, medium stature, and other features that define the genus Tricholoma; it lacks a partial veil, which means there is no ring on the stem; it grows under pines in poor, sandy soil; it has a yellow cap that becomes brownish with age and lacks blackish appressed fibrils; its odor and taste are mealy; and, finally, its gills are yellow. By current definitions Tricholoma equestre occurs in Europe, Asia, and North America—and, within North America, in incredibly diverse ecosystems. However, according to Christensen & Heilmann-Clausen (2013), "[a] complete assessment of T. equestre and allied species, based on a global sampling strategy, and combining molecular and morphological methods, is strongly needed" since there is, according to Heilmann-Clausen and collaborators (2017), "considerable cryptic diversity" in the group. More recent research (Ding et al. 2023) confirms this idea. Compare Tricholoma equestre with Entoloma luridum, which grows in similar habitats but is limited to the upper Midwest and eastern North America; its spore print and mature gills are brownish pink, and it lacks the mealy odor. Tricholoma flavovirens and Tricholoma auratum are synonyms. Description: Ecology: Mycorrhizal with pines; growing alone, scattered, or gregariously in poor, sandy soil; summer and fall; originally described from Sweden (Linnaeus 1753); widely distributed in Europe and North America; reported from Central America and Asia. The illustrated and described collections are from California, Colorado, and Michigan. Cap: 5–10 cm across; convex becoming broadly convex; sticky when fresh, but soon dry; bright greenish yellow when young and fresh, but soon developing a brown to reddish brown center that expands nearly to the margin with age; bald or with a few appressed fibers over the center (but not prominently overlaid with blackish radiating fibers). Gills: Attached to the stem by means of a notch; close; short-gills frequent; pale to bright yellow. Stem: 5–7 cm long; 1.5–2.5 cm thick; more or less equal, or with an enlarged base; bald or finely hairy to subscaly; pale yellow or whitish near the apex, more yellow below; basal mycelium white. Flesh: White; not changing when sliced. Odor and Taste: Mealy. Chemical Reactions: KOH negative on cap surface. Spore Print: White. Microscopic Features: Spores 5–7 x 3–4 µm; ellipsoid; smooth; hyaline in KOH; inamyloid. Basidia 4-sterigmate. Lamellar trama parallel. Hymenial cystidia not found. Pileipellis an ixocutis; elements 2.5–5 µm wide, smooth, hyaline to reddish in KOH. Clamp connections not found. REFERENCES: (Linnaeus, 1753) P. Kummer, 1871. (Quélet, 1886; Kauffman, 1918; Smith, Smith & Weber, 1979; Ovrebo, 1980; Phillips, 1980; Weber & Smith, 1985; Arora, 1986; Riva, 1988; Breitenbach & Kränzlin, 1991; Phillips, 1991/2005; Schalkwijk-Barendsen, 1991; Lincoff, 1992; Shanks, 1996; Barron, 1999; Noordeloos & Christensen, 1999; Roody, 2003; Deng & Yao, 2005; McNeil, 2006; Miller & Miller, 2006; Nonis, 2007; Boccardo et al., 2008; Trudell & Ammirati, 2009; Kuo & Methven, 2010; Bessette et al., 2013; Buczacki et al., 2013; Christensen & Heilmann-Clausen, 2013; Mouhka et al., 2013; Kuo & Methven, 2014; Desjardin, Wood & Stevens, 2015; Evenson, 2015; Siegel & Schwarz, 2016; Cripps, Evenson & Kuo, 2016; Baroni, 2017; Heilmann-Clausen et al., 2017; Christensen & Heilmann-Clausen, 2018; Elliott & Stephenson, 2018; Læssøe & Petersen, 2019; Kibby, 2020; MacKinnon & Luther, 2021; McKnight et al., 2021; Landry et al., 2022; Ding et al., 2023.) Herb. DBG ROMO 2012 5024-14. Herb. Kuo 09140804, 01131104, 01112402. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2024, January). Tricholoma equestre. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/tricholoma_equestre.html |